Step-by-step explanation
We are required to determine the exact value of cos 135°.
Since the angle lies in the second quadrant, we have:
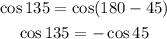
To determine the value of x, we have:
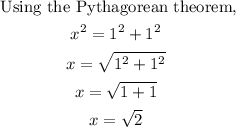
Therefore, the value of cos 135° is:
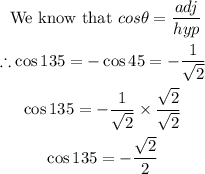
Hence, the answer is:
![\cos(135)\operatorname{\degree}=-(√(2))/(2)]()
The lengths used is the lowest length of sides that can be used.