Step-by-step explanation:
Part a)
By the conservation of energy, we can write the following equation
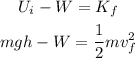
Where m is mass, g is the gravity, h is the height, W is the work done by the force of air resistance, and Vf is the speed at the bottom of the hill.
Replacing m = 85 kg, g = 9.8 m/s², h = 10 m, W = 5 x 10³ J, and solving for Vf, we get
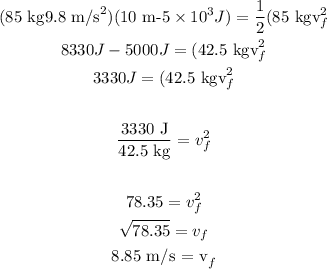
Therefore, the speed at the bottom of the hill is 8.85 m/s
Part b)
We can represent the situation with the following figure
Then, by the conservation of momentum on the x and y-direcction, we can write the following equation
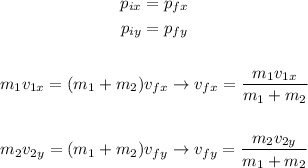
So, we can calculate the final speed on each direction replacing m1 = 85 kg, v1x = 8.85 m/s, m2 = 52 kg, v2y = 4.2 m/s as follows

Then, by the Pythagorean theorem, we get that the speed after the collision is
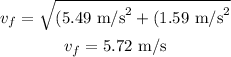
And the direction of the speed is
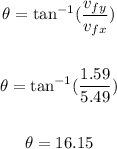
So, the answer is
The speed is 5.72 m/s at a direction of 16.15°