Recall the Pythagorean Theorem:
For a right triangle with legs of lengths A and B and hypotenuse C, the following relation is satisfied:
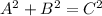
If two variables are known (it could be the hypotenuse and one leg, or both legs), then the third can be calculated. If the hypotenuse is not known, it can be calculated as:
![C=\sqrt[]{A^2+B^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/b9ryy9iydzchpg91mh006dkbhsw408g3f0.png)
If one of the legs is not known, then we can substract the other length squared, and then take the square root:
![\begin{gathered} A^2=C^2-B^2 \\ \Rightarrow A=\sqrt[]{C^2-B^2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/6qr40ptrqc8j1889chb1m58jzkjpjbray4.png)
For problems involving the Pythagorean Theorem, use these equations by replacing the corresponding numerical values of A, B or C. Remember that C does not always stand for the hypotenuse, it always depend on the diagram. For example, if the legs of the right triangle were labelled as X and Y, and the hypotenuse was A, then:
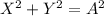
Be careful with that.