Answer:
1.56 m
Step-by-step explanation:
First, we need to find the current in the wire, so we will use the following equation:
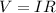
Where V is the voltage, R is the resistance and I is the current. Replacing the values and solving for I, we get:
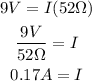
So, the current is 0.17 A.
Now, the magnetic field generated by a wire with current I at a distance r is equal to:
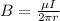
Where μ is 4π x 10^(-7). So, replacing the values and solving for r, we get:
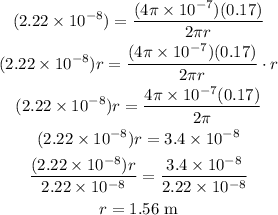
Therefore, the distance is 1.56 m