1.
First, let's find a function that describes this situation.
Let:
t be the temperature of the measuring tape:
L(t) be the lengt of the tape
We'll have that:
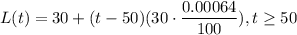
Let's calculate L(100):
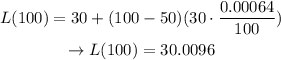
The tape is now 0.0096ft longer
2.
To get the percent error, we divide the original lenght by the expanded lenght, substract that from 1, and multiply by 100:
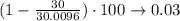
The percent error is 0.03%