Answer:
The change in momentum is 2 times the length of the momentum vector put in the negative direction.
Step-by-step explanation:
The change in momentum is defined as
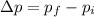
meaning it is the difference between the final and the inital momentum.
Now, our initial momentum is
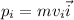
it is in the positive i-direction.
The final momentum is
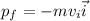
and it is in the negative i-direction.
Therefore, the change in momentum is
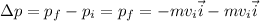
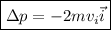
which is our answer!
Now, what is the direction and magnitude of this momentum vector?
This vector has length 2 and points in the negative i-direction.