We have the following function:
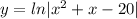
The graph of this function is given by:
We know that a function is increasing is the first derivative is greater than zero. The derivative of the given function is given by
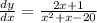
Then, the condition is given by
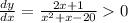
which implies that
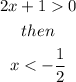
By means of this result and the graph from above, f(x) is increasing for x in:
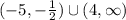
Now, the function is decreasing when
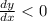
which give us
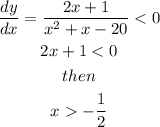
Then, by means of this result and the graph from above, the function is decreasing on the interval:
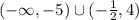
In order to find the local extremal values, we need to find the second derivative of the given function, that is,
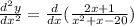
which gives
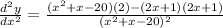
or equivalently
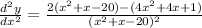
which can be written as
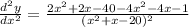
then, we get
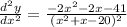
From the above computations, the critical value point is obtained from the condition
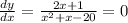
which gives
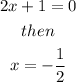
This means that the critical point (maximum or minimum) is located at
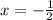
In order to check if this value corresponds to a maximum or mininum, we need to substitute it into the second derivative result, that is,
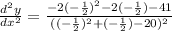
The denimator will be positive because we have it is raised to the power 2, so we need to check the numerator:
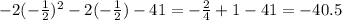
which is negative. This means that the second derivative evalueated at the critical point is negative:
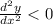
which tell us that the critical value of x= -1/2 corresponds to a maximum.
Since there is only one critical point, we get:
f(x) has a local minimum at x= DNE
f(x) has a local maximum at x= -1/2