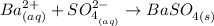Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
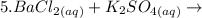
The complete equation is:
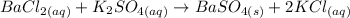
The balanced ionic equation for the reaction is:
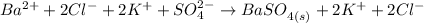
The BaSO₄ is an insoluble solid, so it will not dissociate into ions.
The spectator ions in the reaction are ions that are present at both the reactant side and the product side.
Hence, the spectator ions are:
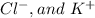
Therefore, the balanced net ionic equation is: