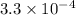Answer: The equilibrium constant is
Step-by-step explanation:
Initial concentration of
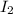 = 0.095 M
= 0.095 M
The given balanced equilibrium reaction is,
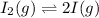
Initial conc. 0.095 M 0 M
At eqm. conc. (0.095-x) M (2x) M
Given : 2x = 0.0055
x = 0.00275
The expression for equilibrium constant for this reaction will be,
![K_c=([l]^2)/([I_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/2r0cf3sqouxdq816tol88s.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get :
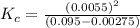
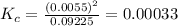
Thus the equilibrium constant is