we have the equation
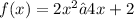
The domain of any quadratic equation is all real numbers
so
The domain is the interval (-infinite, infinite)
To find out the range, we need the vertex
Convert the given equation into vertex form
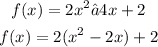
Complete the square
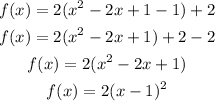
The vertex is the point (1,0)
The vertical parabola opens upward (the leading coefficient is positive)
The vertex is a minimum
therefore
The range is the interval [0, infinite)
All real numbers greater than or equal to zero