Step-by-step explanation
Right triangles are triangles with one right angle i.e. one angle with a measure of 90° so when we deal with this type of figures we know at least one of its internal angles. The opposite side to the right angle is known as the hypotenuse whereas the other two sides are called legs.
Trigonometric functions in right triangles give us the following identities:

We also have the Pythagorean theorem that states that the square of the hypotenuse is the sum of the squares of the legs.
Let's imagine that we have a right triangle like the following:
If we want to find the missing angles A and/or B we need to know at least two sides of the triangle.
For example, if we want to find B and we have b and a we can use the tangent of B and its inverse the arctangent (tan^(-1)):
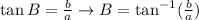
If we know a and c we can find B using its cosine:
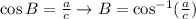
If we know b and c then we can use the sine:
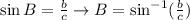
We can also do the same for angle A, we just need to use its corresponding opposite side and adjacent side. And that's how you find a missing angle using trigonometry in a right triangle.
If we are looking for a missing side we can also use trigonometry. In order to find a missing side we need two other sides or another side and an angle. For example, let's assume that we want to find side a.
If we have b and c then we just need to use the Pythagorean theorem:
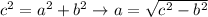
If we have b and A then we can use the tangent of A to built an equation for a:
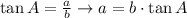
If we have b and B we can use the tangent of B:
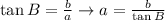
If we have A and c we can use the sine of A:
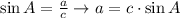
If we have B and c we can use the cosine of B:
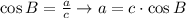
And that's how you find a missing side using trigonometry.