Given the following function f(x):
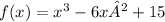
We will use the 1st Derivative Test to find the min/max and intervals of increase/decrease of f(x).
The 1st derivative will be as follows:
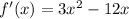
To find the critical points, we will solve the equation f'(x) = 0
![\begin{gathered} 3x^2-12x=0 \\ 3x(x-4)=0 \\ 3x=0\rightarrow x=0 \\ x-4=0\operatorname{\rightarrow}x=4 \end{gathered}]()
We will identify the points using the 2nd derivative:
![\begin{gathered} f^(\prime)^(\prime)(x)=6x-12 \\ x=0\operatorname{\rightarrow}f^(\prime)^(\prime)(0)=-12(-ve)\operatorname{\rightarrow}max. \\ x=4\operatorname{\rightarrow}f^(\prime)^(\prime)(4)=12(+ve)\operatorname{\rightarrow}min. \end{gathered}]()
So the answer will be:
we have a local maximum at x = 0
And a local minimum at x = 4
The intervals of increase will be: (-∞, 0) ∪ (4, ∞)
The intervals of decrease will be: (1,4)