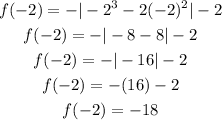Part 1
we have the equation
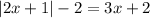
Solve for x
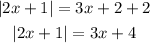
REmember that the absolute value function has two solutions
First solution (case positive)
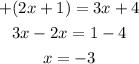
Second solution (negative case)
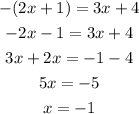
therefore
the solutions are x=-3 and x=-1
Part 2
we have the function
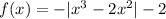
Remember that
f(-2) is the value of f(x) when the value of x=-2
substitute the value of x in the expression above