Answer:
To answer this we use the ideal gas equation:
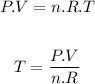
Where:
P is the pressure of the gas (2 atm)
V is the volume of the container (11L)
R is the ideal gas constant (0.0821 L.atm/K.mol)
T is the temperature of the gas
n is the number of moles.
To determine the number of moles we use the carbon dioxide molar mass (44 g/mol)
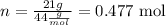
Now we calculate:
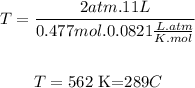
So the answer is:
The temperature of the gas is 289°C