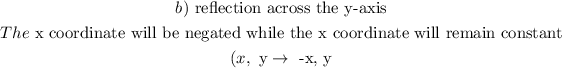Answer:
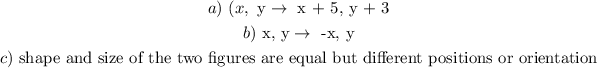
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Two different congruency mapping
To find:
a) a rule for the congruence mapping that will move a figure 5 units to the right and 3 units up
b) a rule for congruence mapping that reflects a figure across the y-axis