In order to calculate the initial velocity, first let's calculate the acceleration generated by this force, using the second law of Newton:
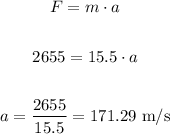
Let's calculate the change in velocity caused by this acceleration in 0.05 seconds:
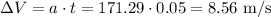
Now, let's draw a diagram to understand the velocity vectors:
Let's calculate the vertical and horizontal components of the final velocity:
![\begin{gathered} V_y=V\cdot\sin135°\\ \\ V_y=45\cdot(√(2))/(2)=31.82\text{ m/s}\\ \\ \\ \\ V_x=V\cdot\cos135° \\ V_x=45\cdot(-(√(2))/(2))=-31.82\text{ m/s}\operatorname{\\} \end{gathered}]()
The horizontal component of the final velocity is equal to the initial horizontal velocity:

The vertical component of the final velocity is equal to the sum of the initial vertical velocity and the velocity added by the acceleration:
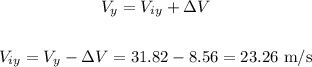
Now, we can calculate the initial velocity using the Pythagorean theorem:
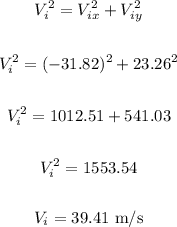
To calculate the direction, we can do the following:
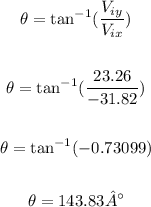
So the direction is N 53.83 W.