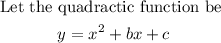
Given that the zeros of the function are at x= 2 and x=6
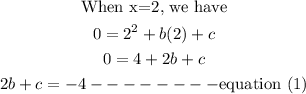
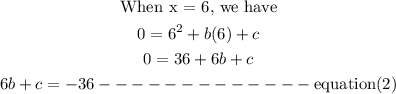
Solving both equations by elimination method, we have
2b + c = -4
6b+c = -36
2b + c-(6b+c)= -4 - (-36)
2b + c-6b-c=-4+36
-4b = 32
b= 32/-4
b= -8
put b= -8 into equation (1)
2b + c = -4
2( -8) + c = -4
-16 + c = -4
c= -4 + 16
c = 12
The function is
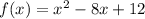
The first missing value is -8, while the second missing value is 12