Step 1 - What weak and strong mean for acids and bases?
A base, according to Arrhenius theory, is a substance that liberates OH(-) in aqueous solution.
OH(-) is the ion responsible for most of the bases properties. Therefore, a strong base will be a base that produces a lot of OH(-) by dissociation.
Usually, strong bases will dissociate completely in water, while weaker bases will ony dissociate partially.
So, for bases like NaOH, for example, we have almost no equilibrium:
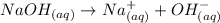
But for weak bases such as NH4OH, we reach equilibrium:
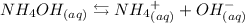
Step 2 - Choosing the right alternative
As the exercise says, NaOH is a strong base. Therefore, it will completely dissociate. By doing so, it will be able to conduct a lot of electricity.
The correct answer is thus item A.
Answer: item A, it will completely dissociate