Answer:
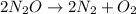
Explanations:
Given the general reaction expressed as:
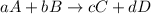
The equivalent rate of reaction is given as;
![-(1)/(a)(\triangle[A])/(\triangle[t])=-(1)/(b)\frac{\triangle{[B]}}{\triangle[{t}]}=(1)/(c)\frac{\triangle{[C]}}{\triangle[{t}]}=(1)/(d)\frac{\triangle{[D]}}{\triangle[{t}]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/n76dshnveyr4lgrjzy90fs4431cnujv86h.png)
Note that the reciprocal of the coefficient at the reactant are negated.
Given the rate relationship;
![-(1)/(2)\frac{\triangle[N_2O]}{\triangle{[t}]}=(1)/(2)\frac{\triangle{[N_2]}}{\triangle{[t}]}=(1)/(1)\frac{\triangle[O_2]}{\triangle[{t]}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/s1lp9yscerbimn0afa2vs8athqesvyeilj.png)
This shows that the compound at the reactant is N2O with a coefficient of 2 while the elements at the product side are N2 and O2 respectively.
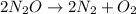
This gives the equaivalent chemical reaction