The Solution.
Representing the given information in a diagram.
Applying Pythagorean Theorem on the right-angled triangle above, we get
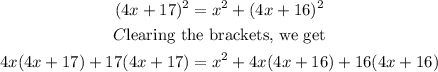
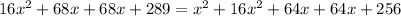
Collecting the like terms, we get
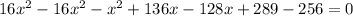
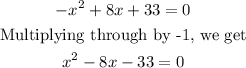
Solving quadratically by factorization method, we get
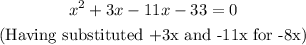
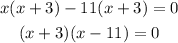
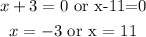
Since the length of a side of a triangle cannot be negative, we discard x = -3.
So, the correct length for the shortest side of the triangle is 11cm
The longer side = 4x+16 = 4(11)+16 = 44+16 = 60cm
The hypotenuse side = 4x+17 = 4(11) +17 = 44+17 =61cm.
Therefore, the correct answer is
11cm, 60cm, and 61cm