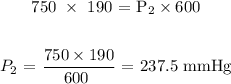Answer:
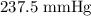
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to calculate the final pressure
According to Boyles' law, the volume of a given mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure
Mathematically:
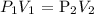
where:
P1 is the initial pressure which is 750 mmHg
V1 is the initial volume which is 190 mL
P2 is the final pressure which is what we want to calculate
V2 is the final volume which is 600 mL
Substituting the values, we have it that: