Recall that the maximum/minimum value of a function is the place where a function reaches its highest/lowest point.
We know that:
![\begin{gathered} For\text{ }all\text{ }x\in[0,2\pi] \\ -1\leq\sin(x)\leq1. \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/9hbk5c1l4mtn3lcxgr6j8utobecaunznjo.png)
Multiplying the above result by 2 we get:
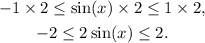
Subtracting 1 from the above inequality we get:
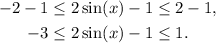
Therefore f(x) reaches a minimum at:
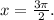
And f(x) reaches a maximum at:
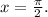
Answer: Option C.