Answer:
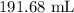
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the final volume
From the general gas equation, we have it that:
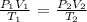
From the question, we have it that:
P1 is the initial pressure which is 513 torr
V1 is the initial volume which is 238 mL
T1 is the initial temperature which we have to convert to absolute value by adding 273.15 K ( 66 + 273.15 = 339.15 K)
P2 is the final pressure that is the same as the initial which is 513 torr
V2 is the final volume that we want to calculate
T2 is the final temperature which is 273.15 K (0 degrees Celsius is 273.15 K)
Substituting the values, we have:
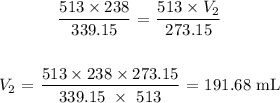
We could have solved this by using Charles' law that relates temperature to volume (volume is directly proportional to temperature)