We have to find the coordinates of the point equidistant from (4,-6) and the origin, as well as on the line 2x-y=9.
We can graph the line and the points to have an idea of the problem:
We can write the distance from our point (x,y) to the point (4,-6) as:
![D_1=\sqrt[]{(x-4)^2+(y+6)^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/r66iibizq1bx61x02eqsy0h9vk1g1r8sex.png)
If we replace y with the value of the equation we get:

![D_1=\sqrt[]{(x-4)^2+(2x-9+6)^2}=\sqrt[]{(x-4)^2+(2x-3)^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/41wlhqhsied3ymoqzx1v2zi58gvvc2chc2.png)
For the distance of our point (x,y) to the origin (0,0) we get:
![\begin{gathered} D_2=\sqrt[]{(x-0)^2+(y-0)^2} \\ D_2=\sqrt[]{x^2+(2x-9)^2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/kxj7m5d5vnlfmxw14s8gq1kmyk7lb61kys.png)
If the point is equidistant to both points, both distances are equal, so we can write:
![\begin{gathered} D_1=D_2 \\ \sqrt[]{(x-4)^2+(2x-3)^2}=\sqrt[]{x^2+(2x-9)^2} \\ (x-4)^2+(2x-3)^2=x^2+(2x-9)^2 \\ (x^2-8x+16)+(4x^2-12x+9)^2=x^2+(4x^2-36x+81) \\ 5x^2-20x+25=5x^2-36x+81 \\ 5x^2-5x^2-20x+36x=81-25 \\ 16x=56 \\ x=(56)/(16) \\ x=3.5 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/xh03djcq6pyfj2ru95srge9d81e8t5yk95.png)
We know the x-coordinate (x=3.5), so we can now calculate the y-coordinate as:
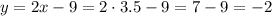
Then, the coordinates for the equidistant point is (3.5, -2)
We can graph this as:
Answer: Coordinates of the point (x,y)=(3.5,-2)