Given data:
CaS Ksp = 8.0x10^-6
CaCO3 Ksp = 3.8x10^-9
Let's start by writing down the chemical equation that refers to each solubility constant.
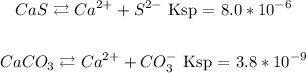
Now let's first discover the concentration of Ca from the solubility of CaS.
![Ksp=[Ca^(2+)][S^(2-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/fwx8ykv48cdzlnrpq9sy4o8gtvq6ps8uen.png)
Since the stoichiometric relation of the two ions in this reaction is 1:1, we can assume the same concentration in mol/L. Let's call this same concentration as letter S for now.
Ksp = S * S
Ksp = S^2
8.0x10^-6 = S^2
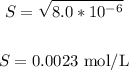
This is the concentration of Ca2+ from CaS.
Now doing the same for CaCO3:
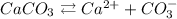
![\begin{gathered} Ksp\text{ = \lbrack Ca}^(2+)][CO_3^-] \\ Ksp\text{ = S*S} \\ Ksp=S^2 \\ 3.8*10^(-9)=S^2 \\ S=\sqrt{3.8*10^(-9)} \\ S=6.2*10^(-5)\text{ mol/L} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/lvufdzk12oxpbt58tcbbmu0bppfnn7vc49.png)
This is the concentration of Ca2+ from CaCO3.
So we have the following final relation of concentrations:
[Ca2+] = 0.0023 + 6.2*10^-5
[Ca2+] = 0.00236 M
[S2-] = 0.00230 M
[CO3 2-] = 6.2*10^-5 M
[Ca2+] = 2.36*10^-3 M
[S2-] = 2.30*10^-3 M
[CO3 2-] = 6.2*10^-5 M
[Ca2+] = 0.00236 M
[S2-] = 0.00230 M
[CO3 2-] = 0.00006.2 M