SOLUTION:
Case: Simiar traiagles
Method:
It is good practice to separate the triangles into the two identifiable similar triangles
Using similar angle scale ratio:
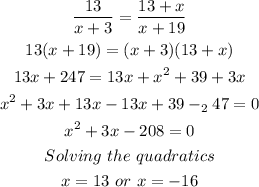
x cannot be -16 because no sides can have negative magnitudes
Hence, x can only be 13.
Final answer:
x= 13