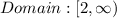 Step-by-step explanation
Step-by-step explanationThe domain of a function is the complete set of possible values of the independent variable,
Step 1
given
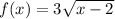
The domain of a radical function is any x value for which the radicand (the value under the radical sign) is not negative Since the square root must always be positive or 0,
so,let's solve for x
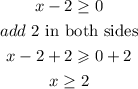
so, the domain is all numbers equal or greater than 2
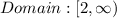
I hope this helps you