Given:
• Initial velocity = 5 m/s
,
• Final velocity = 10 m/s
,
• Initial pressure = 110 kPa
,
• Density = 749 kg/m³
Let's find the value of the final pressure.
Apply Bernoulli's equation:
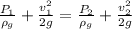
Now, simplify the equation:
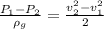
Where:
P1 is the initial pressure = 110 kPa
P2 is the final pressure
v2 is the final velocity = 10 m/s
v1 is the initial velocity = 5 m/s
ρg is the density = 749 kg/m³
Plug in values into the equation and solve for the final pressure, p2.
We have:
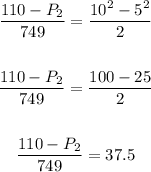
Soling further:
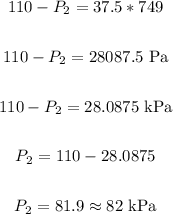
Therefore, the final pressure is 82 kPa
ANSWER:
d. 82 kPa