The formula that relates number of moles, n, and mass, m, is:
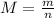
Where M is the molecular weight of the compound we are working with.
In this case, we have Fe₂O₃, and we can calculate its molecular weight using the atomic weghts of Fe (iron) and O (oxygen):
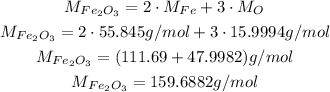
Now, solving the equiation for n and substituting the molecular weight and the given mass, we have:
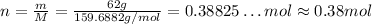
Thus, 62 grams of iron (III) oxide is approximately 0.38 moles.