Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given: Mass of object A,
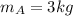 ,
,
Mass of object B,
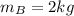 ,
,
The velocity of object A before the collision,
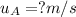 ,
,
The velocity of object A after the collision,
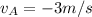 ,
,
The velocity of object B before the collision,
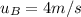 ,
,
The velocity of object B after the collision,
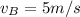 .
.
From the law of conservation of linear momentum,
total momentum of the system before collision = total momentum of the system after collision
Hence,
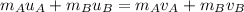
Inserting the values,
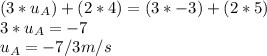
Hence, the initial velocity of object A is -7/3 m/s.