sin2x =12/13
cos2x = 5/13
tan2x = 12/5
STEP - BY - STEP EXPLANATION
What to find?
• sin2x
,
• cos2x
,
• tan2x
Given:
tanx = 2/3 = opposite / adjacent
We need to first make a sketch of the given problem.
Let h be the hypotenuse.
We need to find sinx and cos x, but to find sinx and cosx, first determine the value of h.
Using the Pythagoras theorem;
hypotenuse² = opposite² + adjacent²
h² = 2² + 3²
h² = 4 + 9
h² =13
Take the square root of both-side of the equation.
h =√13
This implies that hypotenuse = √13
We can now proceed to find the values of ainx and cosx.
Using the trigonometric ratio;
![\sin x=\frac{opposite}{\text{hypotenuse}}=\frac{2}{\sqrt[]{13}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/bofhc15ifqh0zgd1ekwybstyyyj9691xod.png)
![\cos x=\frac{adjacent}{\text{hypotenuse}}=\frac{3}{\sqrt[]{13}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/2tcjleh1qx7nwfansowwwh3stwsy0bchzi.png)
And we know that tanx =2/3
From the trigonometric identity;
sin 2x = 2sinxcosx
Substitute the value of sinx , cosx and then simplify.
![\sin 2x=2(\frac{2}{\sqrt[]{13}})(\frac{3}{\sqrt[]{13}})](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/by5vptqjumqcupulgmv5ymqz7mx47h2gi1.png)
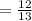
Hence, sin2x = 12/13
cos2x = cos²x - sin²x
Substitute the value of cosx, sinx and simplify.
![\begin{gathered} \cos 2x=(\frac{3}{\sqrt[]{13}})^2-(\frac{2}{\sqrt[]{13}})^2 \\ \\ =(9)/(13)-(4)/(13) \\ =(5)/(13) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/s2be3ybaa7qfru8xop4awji23uak2u0ybf.png)
Hence, cos2x = 5/13
tan2x = 2tanx / 1- tan²x
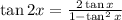
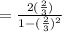
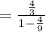
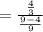
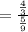
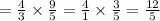
OR
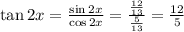
Hence, tan2x = 12/5
Therefore,
sin2x =12/13
cos2x = 5/13
tan2x = 12/5