Answer
Molar mass of the gas sample = 43.9968 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation
The ideal gas law equation is given by
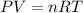
Where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, T is the temperature and R is the molar gas constant.
At STP, T = 273 K and P = 1 atm
Note that the number of moles, n can be rewritten as
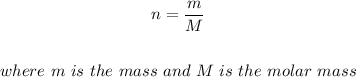
Therefore, the ideal gas law equation above becomes
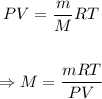
Putting the values of the given parameters below into the formula, we have

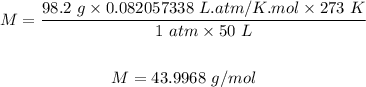
Therefore the molar mass of 98.2 g sample of gas that fills a 50 liter container at STP is 43.9968 g/mol