Given data:
* The wavelength of the incident light is,
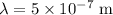
Solution:
The energy of the incident photon is,
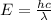
where h is a planck's constant, and c is the speed of light,
Substituting the known values.
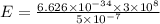
By calculations,
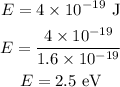
Thus, the energy of an incident photon is 2.5 eV.
Hence, second option is the correct answer.