Given that, there is a 2% of probability that a skier that attempts to run will injure himself on a fall.
You have to calculate the probability that no more than 5 skiers hurt themselves due to a fall in the next 100 skiers that will attempt the run.
This scenario describes a binomial experiment, where:
- The number of trials is fixed: n=100
- The trials are independent of each other.
- The probability of success is constant throughout the experiment, p=0.02
You have to calculate the probability that 5 or fewer skiers get injured, you can express this probability as follows:
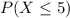
The possible outcomes that are included in this expression are X=5, X=4, X=3, X=2, X=1, and X=0.
So, the probability can be expressed as follows:
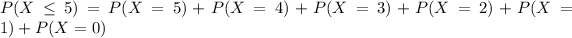
Using the formula of the binomial probability, you can determine each one of the probabilities listed above.
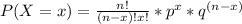
Where
p is the probability of success
q is the probability of failure
n is the sample size
x is the number of successes
For this exercise:
p=0.02
q=1-p=1-0.02=0.98
n=100
-Calculate the probability of x=5
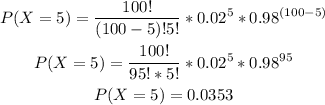
-Calculate the probability of x=4
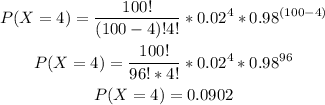
-Calculate the probability of x=3
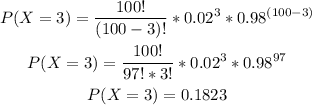
-Calculate the probability of x=2
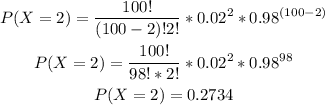
-Calculate the probability of x=1
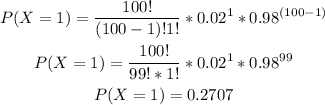
-Calculate the probability of x=0
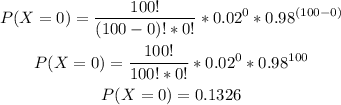
Now you can determine the probability of 5 or fewer skiers getting injured in a fall:
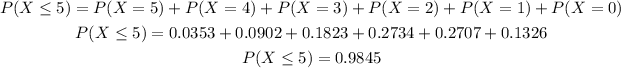
The probability that no more than 5 skiers will suffer an injury is 0.9845.