GIVEN
Two isosceles triangles with two equal pairs of sides are drawn.
SOLUTION
The two triangles have similar sides. The remaining pair of sides are 27 and 26 units respectively.
Note that the angle that subtends the longer side should be greater than the angle that subtends the smaller side. Therefore:
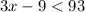
Solving the inequality:
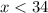
The smaller angle must be greater than 0. This means that:
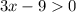
Solving the inequality:
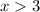
Combining both inequalities:
[tex]3
ANSWER[tex]3