Answer:
Given function is,
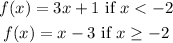
The function 3x+1 and x-3 are continuous function.
To ensure the function f(x) is continuous, we need to show that the function is continuous at the point x=-2.
The function is specified at x = -2,
we get,
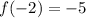
Then we need the limit of the function as x addresses -2 exists.
Consider the left hand limit, we get
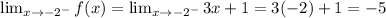
Consider right hand limit, we get
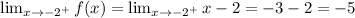
we get that,
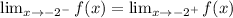
Left hand limit= Right hand limit
The limit of the function as x addresses -2 exists.
Next to check the limit of the function as x addressing -2 is equal to the function value at x = -2
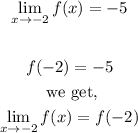
Therefore we get, The limit of the function as x addressing -2 is equal to the function value at x = -2.
Hence the function is continuous at x=-2.
Therefore, the function f(x) is continuous function.
The graph of the function is,