Let A and B be the length of the legs of a right triangle, and C be the hypotenuse.
Then, from the Pythagorean Theorem:
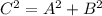
If the missing side is the hypotenuse C, then we can isolate it as:
![C=\sqrt[]{A^2+B^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/b9ryy9iydzchpg91mh006dkbhsw408g3f0.png)
If the missing side is one leg, we can substract the length of the other leg from both sides and take the square root, so:
![\begin{gathered} A=\sqrt[]{C^2-B^2} \\ B=\sqrt[]{C^2-A^2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/fn5ipwd81x27d0o30mvqwfn8yxyic7ycwh.png)