Given:
The given function is
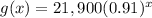
g(x) is the value of a car x years after 2010.
Required:
We need to find the approximate per cent decrease in the value of the car
between 2010 and 2015.
Step-by-step explanation:
Substitute x=0 in the given equation to find the value of the car in 2010.
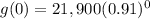
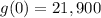
Substitute x=5 in the given equation to find the value of the car in 2015.
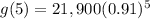
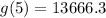
The approximate per cent decrease in the value of the car
between 2010 and 2015.
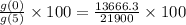
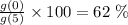
Final answer:
The approximate per cent decrease in the value of the car
between 2010 and 2015 is 62 %.