Answer:
Obtuse-Angled Triangle
Step-by-step explanation:
The Pythagorean Theorem is stated below:
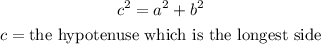
Substitute the given values: 6 cm, 8 cm, 11 cm.
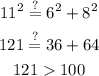
Since we have that:
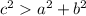
Therefore, we have an obtuse-angled triangle.
Note:
[tex]\begin{gathered} c^2=a^2+b^2\colon\text{Right Triangle} \\ c^2>a^2+b^2\colon\text{Obtuse} \\ c^2