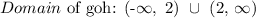
Step-by-step explanation:
(g o h)(x): inserting the values of h(x) into g(x)
g(x) = (x + 6)/(x+ 5)
h(x) = 2x - 9
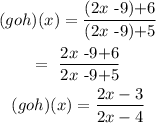
To get the domain of (g o h)(x) = (2x - 3)/(2x -4)
if the value of x = 2
(g o h)(x) = (2x - 3)/(2(2) -4) = (2(2)- 3)/(4-4)
= (4-3)/0 = undefined
This means the domain of x is from negative infinty to number before 2. And from number after 2 to positive infinity. 2 makes it undefined.
In interval notation:
Since 2 is not inclusive, it would have ) instead of ]