We want to know if the following statements are true or false
item a)
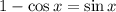
To solve this one, we're going to use the following identity
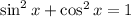
Rewriting this expression "isolating" the sine, we have
![\begin{gathered} \sin ^2x+\cos ^2x=1 \\ \sin ^2x=1-\cos ^2x \\ \sin x=\pm\sqrt[]{1-\cos^2x} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/df4u0ckeq9bxrk0jrrq4ogx13ucj9iw3zd.png)
Using this in our expression, we have
![\begin{gathered} 1-\cos x=\sin x \\ \Rightarrow1-\cos x=\sqrt[]{1-\cos^2x} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/retzt8n9skazev09qbr9spr5k8naxftjzx.png)
When we have a difference of two squares, we can separate them as
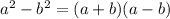
Using this in the argument of the square root, we have
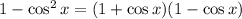
Using this to rewrite our expression
![\begin{gathered} 1-\cos x=\sqrt[]{1-\cos^2x} \\ 1-\cos x=\sqrt[]{(1+\cos x)(1-\cos x)} \\ 1-\cos x=\sqrt[]{(1+\cos x)}\sqrt[]{(1-\cos x)} \\ \frac{1-\cos x}{\sqrt[]{1-\cos x}}=\sqrt[]{1+\cos x} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/mk6bc9svpry0jtvbwlep4brdu8tnebsyq7.png)
We can rewrite the numerator of the left side of the equation as the product of its square root.
![1-\cos x=(\sqrt[]{1-\cos x})^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/v8r1wwr1uh2u60nis7ryyzqihogqcl480w.png)
Using this in our expression, we have
![\begin{gathered} \frac{(\sqrt[]{1-\cos x})^2}{\sqrt[]{1-\cos x}}=\sqrt[]{1+\cos x} \\ \sqrt[]{1-\cos x}=\sqrt[]{1+\cos x} \\ 1-\cos x=1+\cos x \\ -\cos x=\cos x \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ehswa7n9h63p4qnnmypqu34vcigiwsnhpa.png)
Since the cosine of an angle is not equal to minus its value, the first statemente is FALSE.
item b)
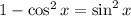
We're going to use the same identity to solve this one.
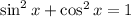
If we substitute the number 1 in our statement for this identity, we're going to have
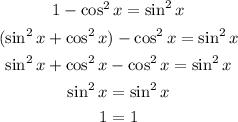
Since we got a true equation in the end, the statement on this item is TRUE.
item c)
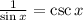
This is a given identity(you can check it is a part of the table above the question), then, it is TRUE.
item d)
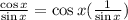
To solve this one, we're going to use the following property.
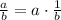
You can take out the numerator as a coefficient for our fraction.
Then, this statement is also TRUE.
item e)
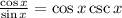
Using the previous two statements, we can solve this one,
Since the statement d is true
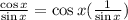
And statement c is also true
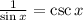
Then, if we substitute c on d, we have statement e, therefore, statement e is also TRUE.
item f)
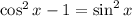
To solve this one, we're going to use the following identity
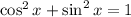
Again, making a substitution, we have
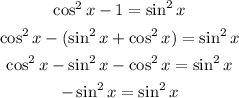
Since the last equation is false, then the statement f is also FALSE.
item g)
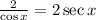
Using the same property used on item d, we have
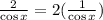
And also using the definition os sec x, we have
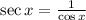
Using those properties in our statement, we have
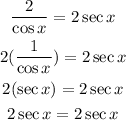
Then, our last statement g is also TRUE.