Solution
- The reation of the acid-base reaction is given below:
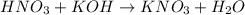
- The number of moles of the base and acid are 1 each from the equation above.
- That is,
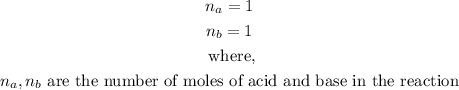
- Next, we can simply apply the formula below to find the molarity of the base KOH.

- Thus, we can find the molarity of KOH as follows:
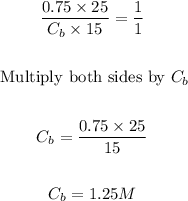
Final Answer
The answer is 1.25M