Given the events A and B
The probability of A is P(A)=2/9
The probability of B is P(B)= 1/3
The probability of the intersection of both events, A and B is P(A∩B)= 1/6
You have to calculate the probability of A occurring, given that B already occurred, to do so you have to use the definition of the conditional probability:
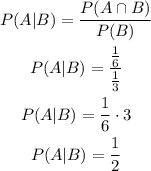
So, the probability of A, given that B occurred is 1/2