To answer this question we first need to know the distance from the crash to the swimmer and the dock.
The distance is given by:
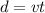
This means that the distance from the crash to the swimmer is:
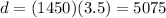
Therefore the crash happened at 5075 meters from the swimmer.
Now, to determine the time it takes the sound to reach the deck we need to determine the speed of sound on air at that temperature, this is given by:
![v=331\sqrt[]{1+(T)/(273)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/dx7fgpct0wcibxzocg0d9sz3ou1pe6ziax.png)
then if the temperature is 20°C we have:
![v=331\sqrt[]{1+(20)/(273)}=342.91](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/85917nehekoeqjy0yy95pp0sfng0jaqphb.png)
Then it takes the sound to reach the deck:
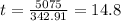
Finally to determine the time it takes after you hear it we subtract the time it takes for you to hear it, then:
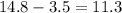
Therefore your friend hear the crash 11.3 seconds after you do.