Answer:
Option E is correct. 320K
Explanations:
In order to get the normal boiling point of the liquid, we will use the Clausius-Clapeyron equation expressed according to the equation:
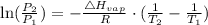
where:
P1 is the vapor pressure of that substance at T1
P2 is the vapor pressure of that substance at T2
ΔHvap is the enthalpy of vaporization.
R is the gas constant - usually expressed as 8.314J/Kmol
Given the following parameters:
![\begin{gathered} P_1=102\operatorname{mm}Hg \\ P_2=760\operatorname{mm}Hg(cons\tan t) \\ T_1=273K \\ \triangle H_{\text{vap}}=30.8\text{kJ/mol} \\ R=8.31\text{J/Kmol} \end{gathered}]()
Substitute the given parameters into the formula to get T2
![\ln (\frac{760_{}}{102_{}}_{})=-\frac{30.8*10^3(J)/(mol)_{}}{\frac{8.31J}{\operatorname{km}ol}}\cdot(\frac{1}{T_2_{}}-\frac{1}{273_{}})]()
Simplify the result to get the value of T2

Hence the normal boiling point of this liquid is approximately 320K