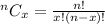Binomial distribution:
The binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution to calculate probabilities of events.
To apply the Binomial distribution first we have to check whether the following four conditions are satisfied or not.
1. There are only two possible outcomes either it is a success or a failure.
For example:
Toss a coin, there are only two outcomes either it is a head or a tail.
2. There is a fixed number of trials.
3. The probability of success/failure does not change from trial to trial.
For example:
The probability of getting heads or tails is the same doesn't matter how many times you toss it.
4. The trials are independent of each other, the outcome of one trial does not affect the outcome of another trial.
For example:
If you got heads in the first trial then it does not have any effect on the second trial and so on.
If all of these conditions are satisfied then we can apply the binomial distribution.
The formula for the binomial distribution is given by
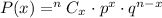
Where n is the number of trials.
p is the probability of success.
q is the probability of failure.
x is the number of favorable outcomes.
nCx is the number of possible combinations.
The probability of winning a race is 0.40.
There are a total of 5 races.
What is the probability of winning two races?
Solution:
Notice that there are only two possible outcomes either you win a race or you don't.
There are a total of 5 races so the number of trials is fixed.
The other two conditions are also satisfied so we can apply the binomial distribution.
Probability of success = p = 0.40
Probability of failure = q = 1 - 0.4 = 0.60
Number of trials = n = 5
Number of favorable outcomes = x = 2
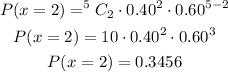
There is a 0.3456 probability of winning two races.