According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, the net force acting on a particle with mass m will cause it to accelerate following the expression:
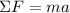
If the net force is equal to 0, then it is automatically deduced that the acceleration of the system must be equal to 0.
Conversely, a condition for a system to be static (when a system does not move) is that the net force acting on it must be equal to 0:
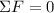
When the net force is equal to 0, there may still be a net torque on the system causing it to rotate. Then, a second equilibrium condition is that the net torque on the system must also be equal to 0:
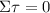
Therefore, the law that described static system is, essentially, Newton's Second Law of Motion.