Presuming that the lines l, m and n are parallel and intersecting a single line, the angles measuring 132° and (x + 13)° appears to be a pair of Alternate Interior Angles.
Under this relationship, the two angles must be congruent.
Therefore,
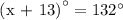
Let's determine the value of x,
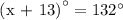
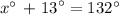
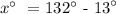
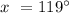
Therefore, x = 119°