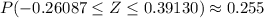Given a normal random distribution with mean μ and standard deviation σ:
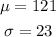
The z-score can be calculated using the formula:
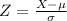
Where X is a value of the normal random distribution. We need the probability that a randomly selected utility bill is between $115 and $130. The z-scores of these values are:
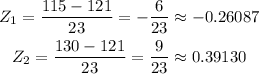
Then, we need to calculate the probability of:
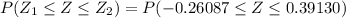
Using the tables of the z-distribution, this probability is: