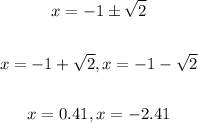Solution:
Given the equation;
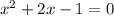
Using completing the square method; take one to the other side of the equation and change the sign.
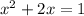
Add the square of half of the coefficient of x to both sides of the equation;
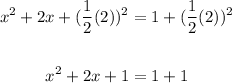
Factorize the left side and simplify the right side;
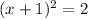
Thus, the form is;
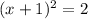
And the solution is;